Top 10 OSHA Violations for 2025
During the 2025 National Safety Council’s Safety Congress and Expo (opens in a new tab) in September 2025, OSHA released preliminary data and the list of the 10 most frequently cited standards for fiscal year 2025. There was a general decrease in citations of the “top 10” from FY2024, but there is always room for improvement. Employers can encourage a safe working environment with enhanced educational programs, internal inspections and enforcement strategies. Learn more about these frequently-cited violations and what your organization can do to avoid becoming an OSHA statistic.
Please note that injury and fatality data lags behind citation data. Cited injuries and fatalities use the latest available numbers.
-
Fall Protection – General Requirements (1926.501) – 5,914 Violations
Fall protection tops the list for the 15th year in a row, and it’s for good reason. Falls continue to be a leading cause of workplace accidents and deaths. In 2023, 725 people died due to falling to a lower level. Standard 1926.501 is designed to protect employees on walking or working surfaces with an unprotected side or edge above 6 feet.
Fall protection tips:
- Post safety signs to warn of danger or hazards
- Keep absorption products readily accessible to clean up spills immediately
- Use handrails, safety nets and other protective devices
- Keep ladder rungs, feet and steps clean and dry and observe load limit
Learn more about the OSHA Fall Protection Standard (opens in a new tab) and standard 1926.501 (opens in a new tab).

-
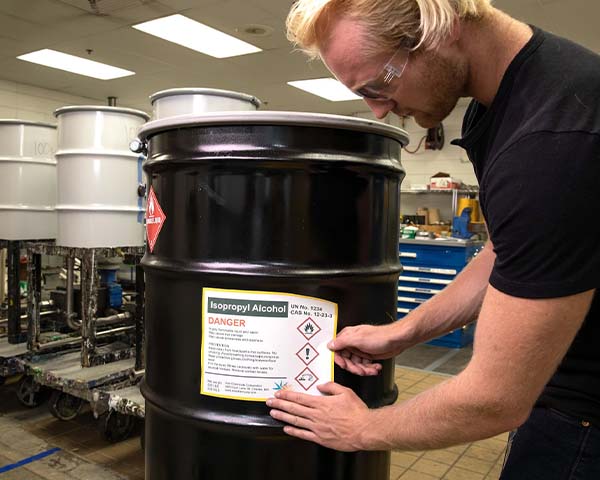
Hazard Communication (1910.1200) – 2,546 Violations
Chemical accidents can turn deadly quickly, and it can happen on a large scale. In 2023, mishandling chemicals accounted for 63 on the job fatalities. Standard 1910.1200 helps ensure that hazardous chemicals are properly identified and safety data sheets are readily available and understandable for workers. The standard applies to chemicals produced in the workplace as well as those imported into the workplace.
Chemical safety tips:
- Maintain a master chemical list using SDS binders or chemical database software
- Use proper labeling or bring GHS label printing in-house
- Train employees about chemical safety
- Learn the standard and maintain a written hazard communication program
Learn more about the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard and OSHA Standard 1910.1200.

-
Ladders (1926.1053) – 2,405 Violations
Ladders are some of the most common pieces of workplace equipment. But their ubiquity, ease of use and limited qualification requirements put workers in dangerous situations where manufacturer recommendations and safe ladder practices are ignored. In 2023, portable ladders and stairs were the primary cause of 109 fatal work injuries (opens in a new tab).
Ladder safety tips:
- Position ladders on a stable, level surface
- Use three points of contact
- Do not exceed the maximum load rating of the ladder
- Keep maintenance regular and recorded with ladder inspection tags
Learn more about the OSHA Ladders Standard 1926.1053(opens in a new tab).

-
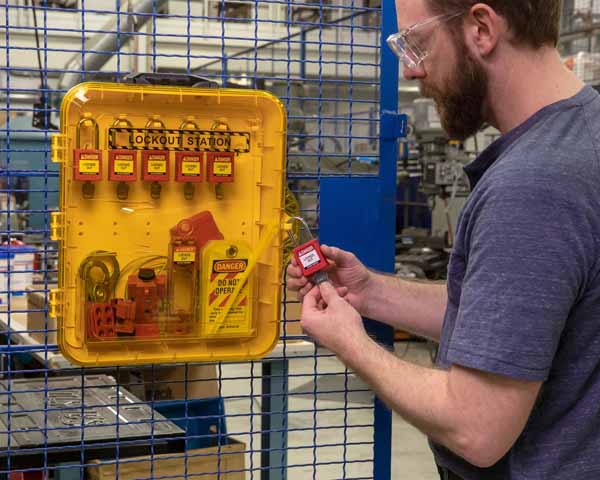
Lockout Tagout (1910.147) – 2,177 Violations
OSHA’s Control of Hazardous Energy regulation, commonly referred to as lockout tagout, requires that energy sources be contained during servicing and maintenance to prevent accidents. When hazardous energy sources are not properly controlled, workers servicing or maintaining equipment can be seriously injured or killed. Hazardous energy was the cause of 190 deaths in 2023 with 142 of those fatalities caused by electrical exposure.
Lockout tagout safety tips:
- Develop and document a LOTO program and policy
- Write machine- or task-specific lockout tagout procedures
- Identify and mark energy isolation points
- Conduct LOTO training
- Provide proper lockout tagout devices and safety padlocks
- Sustain your program and procedures
Learn more about OSHA's Control of Hazardous Energy Standard 1910.147(opens in a new tab).

-
Respiratory Protection (1910.134) – 1,953 Violations
OSHA requires employers to develop and implement a written respiratory protection program. This includes situations in which permissible exposure limits (PELs) of airborne contaminants are exceeded and the requirements for respirator requirements — including selection, employee training, fit testing, medical evaluation, use, cleaning, maintenance and repair — are not followed. There were 125,400 reportable cases of respiratory illness in 2023.
Respirator safety tips:
- Post signs to warn of danger or respirator-required areas
- Have a written program in place
- Provide the correct respirators, training, fit testing and medical evaluations
- Ensure proper care, maintenance and use of respirators
Learn more about Respiratory Protection Standard(opens in a new tab).

-
Fall Protection – Training Requirements (1926.503) – 1,907 Violations
Beyond fall arrest systems and hazard communication, fall protection training is key to preventing workplace accidents. OSHA regulations require fall protection training for any worker that goes up 6 feet or higher.
The training includes recognizing fall hazards, the correct procedures to minimize hazards, equipment limitations and proper use. Training must be certified by a competent person and retraining must occur if equipment or conditions change. Our Slips, Trips, and Falls guide provides resources that can help prevent falls in the workplace.
OSHA’s Fall Prevention Training Guide(opens in a new tab) gives tips for how to conduct trainings, called “Toolbox Talks,” including to keep them:
- Short – Each Toolbox Talk should last approximately 5 to 10 minutes
- Participatory – Allow workers to ask questions and discuss the topic
- Easy to follow – Avoid jargon, confusing and irrelevant topics or instructions
Learn more about OSHA’s Fall Protection – Training Requirements Standard 1926.503(opens in a new tab).
-
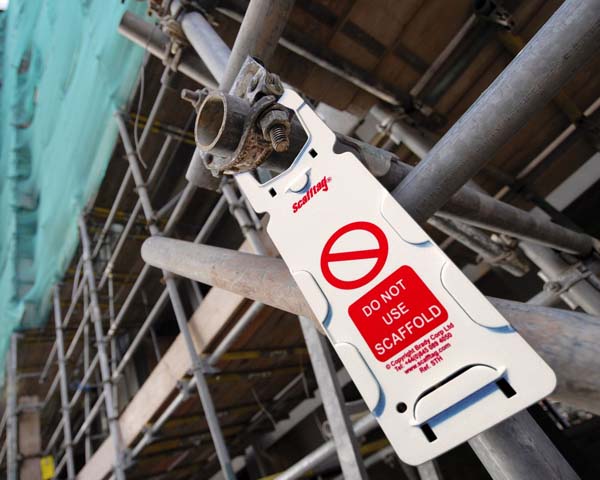
Scaffolding (1926.451) – 1,905 Violations
OSHA scaffolding regulations seek to minimize falls and falling objects on or near scaffolding. Many citations relate to issues of inadequate or missing guardrail systems, fall protection and foundations for poles, legs, posts, uprights and frames.
Scaffolding safety tips:
- Ensure scaffold deck is fully floored, level and can support its intended load
- Use fall protection devices, such as guardrails, toeboards, screens and netting
- Maintain regular inspections and training
- Identify key safety and compliance information via scaffold tags
Learn more about scaffolding safety.

-
Forklifts and Powered Industrial Trucks (1910.178) – 1,826 Violations
You’d be hard-pressed to find facilities and industries that don’t use powered industrial trucks, like forklifts or lift trucks. But their heavy weight, powerful capabilities and operation in busy or narrow areas can make them dangerous. Forklifts, order pickers, platform trucks, and other powered industrial tricks were the primary cause of 67 workplace fatalities in 2023.
OSHA requires that forklift operators be over the age of 18 and go through proper training and licensing. They are also subject to performance evaluations and refresher training.
Powered industrial truck safety tips:
- Wear seatbelts
- Never exceed the rated load and do not raise or lower the load while traveling
- Keep a safe distance from platform and ramp edges
- Use horns at cross aisles and obstructed areas
- Lock out forklifts during service and repair
- Post signs to warn of forklift traffic and directions
- Use floor tape to mark aisles and passageways and keep them clear of hazards
- Read this article on heavy equipment safety for more tips on heavy machinery safety
Learn more about OSHA’s Powered Industrial Trucks Standard(opens in a new tab) and OSHA Standard 1910.178(opens in a new tab).

-
Personal Protective and Lifesaving Equipment, Eye and Face Protection (1926.102) – 1,665 Violations
Eye injuries are largely preventable with the proper protection. Still, thousands of workers are injured or blinded every year. OSHA requires eye and face protection to be provided whenever necessary to protect workers against chemical, environmental, radiological and mechanical irritants and hazards.
Eye and face protection safety tips:
- Ensure eyewear fits properly and is designed for the specific hazard
- Eyeglass wearers should have safety equipment that fits over glasses
- Clean and disinfect eyewear before storage
- Use face shields with protective eyewear
- Remind employees when PPE is needed with PPE signs
Learn more about OSHA’s Eye and Face Protection Standard(opens in a new tab) and OSHA Standard 1926.102(opens in a new tab).

-
Machine Guarding (1910.212) – 1,239 Violations
Moving machine parts can crush fingers, hands, feet and other extremities. These injuries can lead to amputations and reduced use of the body part. Accidental contact can also cause burns, cuts and eye injuries. Machine guarding helps prevent these incidents by physically preventing accidental contact of machine parts or debris by operators or others in the immediate vicinity.
Machine guarding safety tips:
- Keep employees informed with machine operation signs
- Don’t adjust or remove guards without proper authorization
- Ensure machine guards are in place before starting machinery
- Train employees to recognize incomplete, ineffective or missing machine guards
- Ensure minor servicing procedures are up to date
Learn more about OSHA’s Machine Guarding Standard(opens in a new tab) and OSHA Standard 1910.212(opens in a new tab).

